1. Introduction
Hello! We are a writer team from Definer Inc.
Zero Trust Security is an approach to cybersecurity that emphasizes a strict and continuous verification process for every user, device, and network connection, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the corporate network perimeter. This security model assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default, and access to resources is granted based on explicit authentication and authorization. Azure, the cloud computing platform by Microsoft, provides a comprehensive set of tools and services to implement and achieve Zero Trust Security.
In this issue, you are wondering about the use of Zero Trust Security in Azure.
Let's take a look at the actual screens and resources to explain in detail.
2. Purpose/Use Cases
This article summarizes information and practices that can be helpful when you want to achieve zero-trust security in Azure.
- Minimizing the Attack Surface: Zero Trust Security reduces the attack surface by eliminating implicit trust and verifying every access request. It prevents unauthorized users or compromised devices from gaining access to sensitive resources, reducing the risk of data breaches and insider threats.
- Identity and Access Management: Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) plays a crucial role in Zero Trust Security. It enables secure authentication, identity verification, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for users. With Azure AD Conditional Access policies, organizations can enforce granular access controls based on user context, device health, and other parameters.
- Network Segmentation: Azure Virtual Network (VNet) and Azure Firewall allow organizations to implement network segmentation and micro-segmentation. By dividing the network into smaller security zones and enforcing strict access controls between them, organizations can limit lateral movement of threats and contain potential breaches.
- Secure Connectivity: Azure Virtual Private Network (VPN) and Azure ExpressRoute provide secure connectivity options to connect on-premises networks with Azure resources. By encrypting data in transit and implementing secure connection protocols, organizations can ensure that communication channels are protected against interception and unauthorized access.
- Threat Detection and Monitoring: Azure Security Center provides advanced threat detection capabilities, leveraging machine learning and AI algorithms to identify and respond to security threats. It offers real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and security recommendations to help organizations detect and mitigate potential security risks.
- Data Protection: Azure Information Protection and Azure Key Vault enable organizations to encrypt and protect sensitive data, both at rest and in transit. With Azure Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies, organizations can implement data classification and control mechanisms to prevent data leakage or unauthorized access.
- Compliance and Governance: Azure provides a range of compliance certifications and frameworks to support regulatory requirements. With features like Azure Policy and Azure Advisor, organizations can enforce compliance controls, perform continuous compliance assessments, and ensure adherence to security best practices.
By implementing Zero Trust Security with Azure, organizations can establish a robust security framework that enhances data protection, reduces the risk of security breaches, and provides granular control over access to critical resources. It aligns with modern security requirements and helps organizations stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
3. What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero-trust security is the concept of taking security measures based on the premise that nothing is to be trusted, in accordance with the sexual misconduct theory.
Conventional security divides trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, and measures are taken at the boundaries between them.
However, with the spread of cloud computing and other services, it is no longer unusual for resources to be scattered across external networks that need to be protected.
Based on the premise that all communications should be treated with suspicion, Zero Trust provides a variety of security measures, including network encryption, enhanced user authentication and authorization through multi-factor authentication and appropriate authorization, and integrated log monitoring of networks and devices.
The zero-trust concept itself was proposed in the United States in 2010.
In recent years, the spread of remote work associated with the new coronavirus and the resulting increase in security risks have further increased attention to Zero Trust.
4. Zero-trust security in Azure
Azure also strongly recommends zero-trust security following the following principles
・Explicitly validate
Authentication should be performed using appropriate service and device policies. Authentication is the process of verifying that a device, user, etc. is authentic.
This includes, for example, enabling two-step authentication.
Authorization is also required with appropriate services and access policies. Authorization is the process of granting privileges to specific subjects.
Use minimal privileged access
Access policies, for example, should grant the minimum necessary functions to users and applications.
Refrain from easily granting administrative privileges, etc. User secrets should also be issued as little as possible.
Assuming a breach
To minimize the scope of impact, the architecture should be designed so that access can be segmented.
Ensure that each component is encrypted end-to-end with each other, and implement proactive defense measures through analysis and threat detection.
Below are the key elements of Zero Trust.
(From Microsoft Zero Trust Architecture)
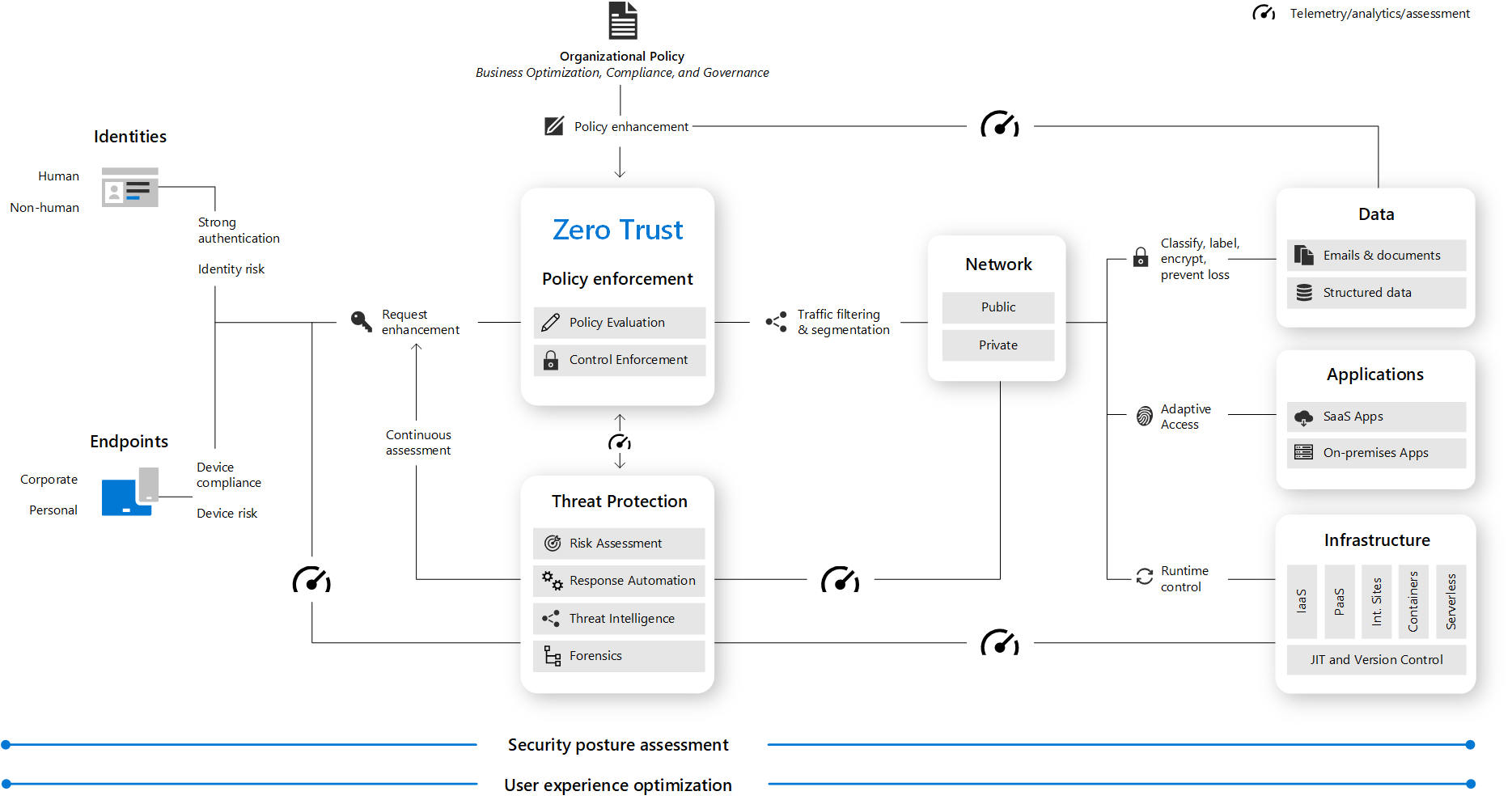

5. Cited/Referenced Articles
Zero Trust Security
VMware Workspace ONE for Zero Trust Security ...
Securing Privileged Access Accounts | Microsoft Docs
Zero Trust Security Solutions | Entrust IAM Solutions
Zscaler: The Leader in Zero Trust
How to Achieve Zero Trust Security? ~ Free "Initiatives ...
What is Zero Trust? Advantages and disadvantages, and how to achieve ...
What is Zero Trust Security? Merits and cautions for implementation are also explained.
6. About the proprietary solution "PrismScaler"
・PrismScaler is a web service that enables the construction of multi-cloud infrastructures such as AWS, Azure, and GCP in just three steps, without requiring development and operation.
・PrismScaler is a web service that enables multi-cloud infrastructure construction such as AWS, Azure, GCP, etc. in just 3 steps without development and operation.
・The solution is designed for a wide range of usage scenarios such as cloud infrastructure construction/cloud migration, cloud maintenance and operation, and cost optimization, and can easily realize more than several hundred high-quality general-purpose cloud infrastructures by appropriately combining IaaS and PaaS.
7. Contact us
This article provides useful introductory information free of charge. For consultation and inquiries, please contact "Definer Inc".
8. Regarding Definer
・Definer Inc. provides one-stop solutions from upstream to downstream of IT.
・We are committed to providing integrated support for advanced IT technologies such as AI and cloud IT infrastructure, from consulting to requirement definition/design development/implementation, and maintenance and operation.
・We are committed to providing integrated support for advanced IT technologies such as AI and cloud IT infrastructure, from consulting to requirement definition, design development, implementation, maintenance, and operation.
・PrismScaler is a high-quality, rapid, "auto-configuration," "auto-monitoring," "problem detection," and "configuration visualization" for multi-cloud/IT infrastructure such as AWS, Azure, and GCP.

